¶MVC配置
实际上想要了解关于mvc配置的最简单方式就是阅读
web.servlet.config包代码,该包代码描述的xml配置方式对于<mvc:>标签的解析方式
web.servlet.config.annotation描述使用注解,抛弃xml的方式如何配置mvc
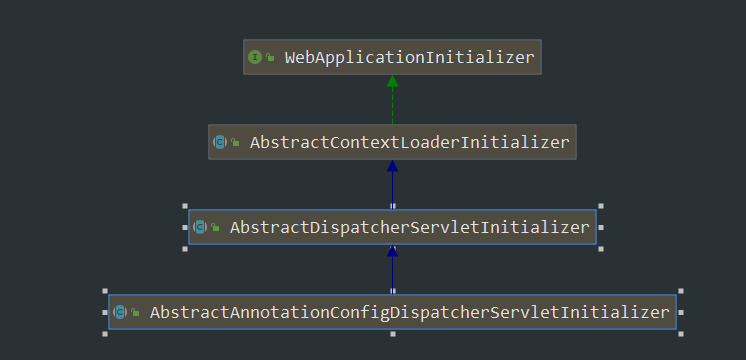
¶WebApplicationInitializer体系
简单来说该体系用来使用注解方式确定ioc和mvc容器入口
- SpringServletContainerInitializer接口
该接口是ServletContainerInitializer,由servlet标准定义,该接口会将所有WebApplicationInitializer调用 - WebApplicationInitializer辅助类
WebApplicationInitializer.png 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79//--------------------AbstractContextLoaderInitializer------------------------
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
//创建ioc容器,并且注册监听器
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
//------------------------AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer---------------------
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
//注册mvc容器,并且创建FrameworkServlet,并且将该servlet设置为1级启动
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
//-----------------------AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer------------------------
//由用户指定ioc和mvc容器的根类,并且可以知道这种情况下mvc框架内部的context是AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
//xml配置时不是这种context
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(configClasses);
return context;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}
//用户来指定ioc和mvc容器 根类
protected abstract Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses();
protected abstract Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses();
¶WebMvcConfigurer体系
简单来说该体系用来详细的确定mvc内部组件,由用户来个性化
- WebMvcConfigurationSupport:实际上属于javaConfig,是一个父类
- handler和mapping的创建,并为子类留下实现位置
- 异常处理器
- 默认的conversionService
- …
- DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
//spring中典型的Composite,包含WebMvcConfigurer列表
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// WebMvcConfigurer获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer
(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
}
//这就是WebMvcConfigurationSupport留下的接口位置
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addInterceptors(registry);
} - WebMvcConfigurer:用户实现
¶springBoot对于mvc注解配置的运用
xxxx
¶springMVC概念
在mvc框架中我们所要关注的点为控制器函数入参解析,回参解析,以及视图和模型
¶模型
ModelAndViewContainer:作为形参在入参处理,回参,过程中传递,包含了view,model,以及一些状态Model:实际上在spring的概念中本质就是一个集合,在单次请求处理过程作ModelAndView:包含Model和View,Adaptor的处理结果,会继续交由dispatcherServlet进行处理,进行视图渲染DataBinder:数据绑定(bind)的概念,实质是通过spring内省技术将pvs赋值到target中[1]@InitBinder- 该注解只能用作于函数上,表示该函数要对此次mvc请求过程中创建的
DataBinder进行设置从而会引发,入参,或回参过程
中的数据绑定(bind)和类型转换(converte),数据验证(valid) - 该注解会生效的情况
- NamedValueMethod类型注解入参处理后的
类型转换 @ModelAttribute处理入参,并且该请求模型在MVCContainer中不存在,即新创建模型时会使用bind功能,以及valid功能@RequestPart和@RequestBody做valid功能RedirectAttributes作为形参时,传递
- NamedValueMethod类型注解入参处理后的
- 该注解只能用作于函数上,表示该函数要对此次mvc请求过程中创建的
¶入参解析
这部分内容是根据HandlerMethodArgumentResolver体系整理的
¶NamedValueMethod
这个名字根据入参解析器的父类AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver命名,这类注解一般都有共同点,
由name,value,defaultValue构成
-
列举
- RequestHeader
- RequestAttribute
- RequestParam
- CookieValue
- MatrixVariable
- SessionAttribute
- Value
- PathVariable
-
支持Optional表示(4.0以上)
1
2
3
4
5("/test3")
public void test3(@RequestParam("name") Optional<String> name) {
System.out.println(name);
}
- 注意如果不使用springBoot,则需要主动配置一个能完成T->Optional的转换器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//这样配置是因为spring本身没有给FormattingConversionService预留创建点,它默认创建无法转换T->Optional
public class MvcConfig extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration {
public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {
FormattingConversionService formattingConversionService = new WebConversionService(null);
addFormatters(formattingConversionService);
return formattingConversionService;
}
}
- 关于
CustomEditorConfigurer,这玩意是对BeanFactory中创建的BeanWrapperImpl使用的,从它所在的包就能看出来
- 注意如果不使用springBoot,则需要主动配置一个能完成T->Optional的转换器
-
使用el表达式
- 注解中含有
name属性,default都可以使用el表达式 @Value如果使用在形参上可以直接使用el表达式1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18//
public class BeanT {
private final String name = "test";
private final String nameValue = "testValue";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getNameValue() {
return nameValue;
}
}
//
("/test2")
public void test2(@RequestParam(value = "#{beanT.name}", defaultValue = "#{beanT.nameValue}") String name,@Value("#{beanT}") BeanT beanT) {
System.out.println(name);
}
- 注解中含有
-
@RequestAttribute和RequestParam的区别
简单的来说就是后者表示servlet api中的请求参数,后者则是spring对HttpServletRequest又做了一层封装,获取这其中的属性,这个map在mvc流程做了很多工作 -
MatrixVariable:实际上就是url中使用;分割key-vlaue而不是&
- 开启矩阵变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class MvcConfig extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration {
protected void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper=new UrlPathHelper();
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false); //这个属性
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
}xml使用
<annotation-driven enable-matrix-variables="true" />,可以观察源码,实际上处理mapping的中urlPathHelper的一个变量- 使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//url:http://localhost/test4/path;key1=123;key2=333/next/p2;key1=222;key2=3333
("/test4/{path}/next/{path2}")
public void test4(@MatrixVariable(value = "key1", pathVar = "path") String key1, @MatrixVariable MultiValueMap<String, String> map, @MatrixVariable(value = "key1",pathVar = "path2") String key12) {
System.out.println(key1); //123
System.out.println(key12); //222
System.out.println(map); //key1:[123,222],key2:[333,3333]
}
- `pathVar`属性要和`{}`路径一起使用,解析器源码比较简单
- map类型可以不带`pathVar`表示获取全部矩阵,String类型最好带上,否则会因为如果不同的`{}`路径出现两个相同key异常,如上
- map如果不是MultiValueMap类型则只能获取到一个`{}`路径中的矩阵
¶map类型
一般来说Map类型分两种,Map类型和MultiValueMap,后者内部是一个Map<String,List<Object>>
Map形参:获取mvcContainter中所有的model属性@PathVariable和Map:获取占位符路径@RequestHeaderMap:获取所有的请求头键值对,但是value只能拿到第一个MultiValueMap:可以获取所有
@RequestParamMultiValueMapMultiValueMap<String,MultipartFile>:获取多文件上传的所有文件MultipartFile<String,Part>:获取所有的PartMultipartFile:获取所有请求参数,value是一个list
Map
-Map<x,MultipartFile>Map<x,Part>Map
@MatrixVariableMap:获取的value为第一个MultiValueMap:获取单一key的所有
¶ModelAttribute注解
- 使用位置
- 方法:表示该函数要创建一个model
- 参数:表示要获取一的model#value
- Type典型使用
- 使用返回值创建model
- 使用形参创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Controller1{
public String genMod1(){
return "value"
}
public void genMod2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("key","value");
}
} - 两者区别:前者model的key由mvc生成,并且必须是该key之前不存在才能创建这个key-vlaue,后者可以覆盖
- Para典型使用
- 获取mvcContainer中model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17("/test")
public void test(@ModelAndView("key")String key){
}
```
- 特别点
- 当所有的`ModelAttribute`函数执行结束后,在真正调用控制器函数前,若改控制器上有参数带有``并且
和`SessionAttributes`中任意name相同,则会从session中再次获取对应的值放置到mvcContainer中,若此时session没有则
抛出异常
- 当``和``同时使用,前者无效
##### Errors
该类实际上是mvc中数据绑定和验证过程中存放信息的类,典型子类`BindResult`
```java
("/test")
public void test(@Valid User,BindResult bind){
}
- 获取mvcContainer中model
¶Servlet相关
¶ServletResponse
三种参数
- ServletResponse
- OutputStream
- Writer
¶ServletRequest
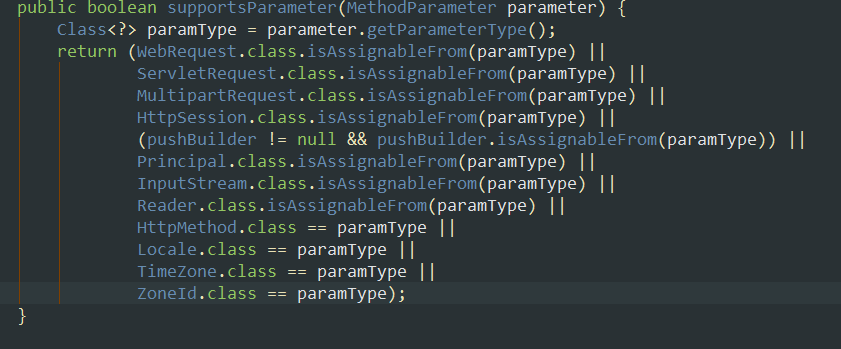
¶MessageConvertor类型
¶@RequestBody
使用该注解明确表示要使用消息转换器处理,具体参考消息处理器
¶其他
¶Errors
spring中的接口,典型的为BindingReuslt,记录了DataBinder的bind操作过程中的错误
- 位置:在形参中要放置在
@ModelAttribute,@RequestBody,@RquestPart之后,简单来说就是在发生了
bind之后
¶SessionStatus
SessionStatus,spring提供
¶RedirectAttributes
RedirectAttributes,一般和redirect:一起使用,这里的属性会被传递到前台,302之后的请求会带上这个key-value
,spring内部实现,使用了FalshMap
- 参考
1 | ("redirect/{red}/test/{red2}") |
¶回参处理
回参处理只能发生在SerlvetInvokeHandMethod中,已经是属于控制器方法调用了
¶视图
¶字符串
字符串会被认为是viewName,在DispatcherServlet的视图处理部分进一步处理
¶View
直接返回View类,在视图处理代码中,会直接调用该视图渲染
¶模型
这里和@ModelAttribute标记的方法做区别开来
¶Map
将map添加到MVCContainer中
¶Model
同上
¶ModelAndViewContainer
¶消息处理器
¶ResponseBody
明确使用消息处理器,这样的回参处理,正常情况下都不应该进行视图处理
会将mvc过程中的MVCContainer属性转移到这个中,并且将handle过程标记为结束
¶ControllerAdvice
该注解标记的类会被当做对于任意控制器的增强,提供了对于DataBinder初始化处理,
构建model,以及异常处理
¶@InitBinder和@ModelAttribute
- @InitBinder
- 被该注解描述的函数,形参只能是一个
DataBinder或其子类 InitBinder#value,表示对哪一个model的DataBinder进行初始化,若没有该value,则任意情况下都会执行- 不能有返回值
- 参考WebDataBinder
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class ControllerAdciceTest{
("user") //表示该函数仅仅对user属性有作用
public void init(WebDataBinder dataBinder) {
dataBinder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("test.") //model处理res的参数时会添加上这个前缀
}
}
- 被该注解描述的函数,形参只能是一个
- @ModelAttribute
在ControllerAdvice中也会被全局执行
¶ExceptionHandler
参考handler异常处理总结部分.
¶BodyAdvice
- 调用点分别在
httpMessage入参和回参处理器中,参考适配器初始化 - 使用必须配合
ControllerAdvice注解 - 代码参考
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class ResRepAdvice implement RequestAdvice,ResponseAdvice{
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return false;
}
public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) throws IOException {
return null;
}
public Object afterBodyRead(Object body, HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return null;
}
public Object handleEmptyBody(Object body, HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return null;
}
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return false;
}
public String beforeBodyWrite(String body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
return null;
}
}
¶其他注解
¶ResponseStatus
该注解有两个使用情况
- 标记在控制器:
- 在
ServletInvokeHandlerMethod,可能会导致回参处理跳过,源码参考ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
- 在
- 标记在异常中
- 和
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver结合使用,参考ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
- 和
- 接口定义


