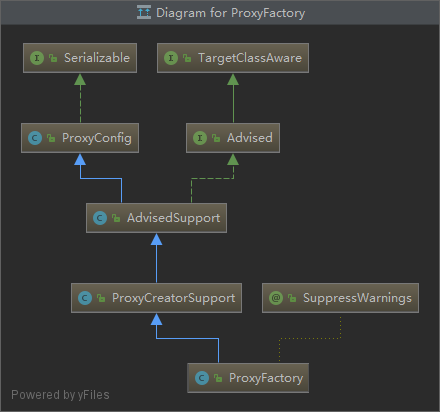
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
| public CglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");
if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {
throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified");
}
this.advised = config;
this.advisedDispatcher = new AdvisedDispatcher(this.advised);
}
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
Callback targetInterceptor;
if (exposeProxy) {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
else {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ?
new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
aopInterceptor,
targetInterceptor,
new SerializableNoOp(),
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();
Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];
this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<>(methods.length);
for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(methods[x], rootClass);
fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(
chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());
this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(methods[x].toString(), x);
}
callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];
System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);
System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);
this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;
}
else {
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
|